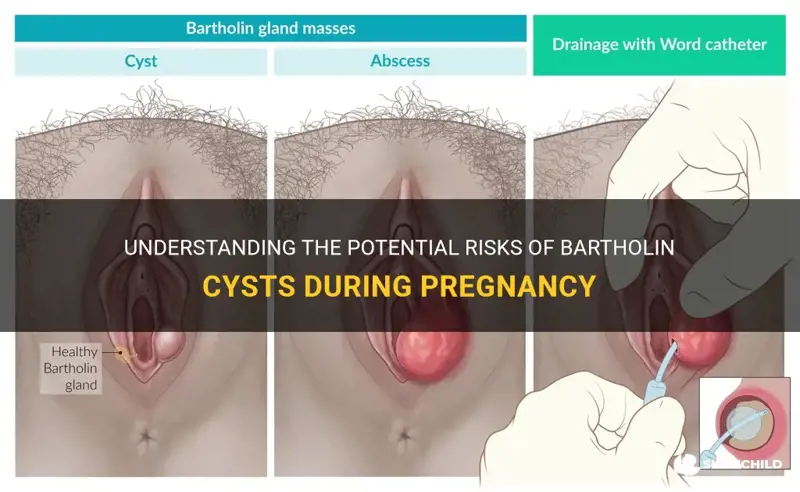
During pregnancy, women may experience various changes and symptoms due to hormonal fluctuations. One of these potential changes is the development of a Bartholin cyst, which is a small, fluid-filled sac that forms near the opening of the vagina. While Bartholin cysts are usually benign and harmless, they can sometimes cause discomfort and complications during pregnancy. In this article, we will explore whether Bartholin cysts can be dangerous during pregnancy and what steps can be taken to manage them effectively.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Common during pregnancy | Yes |
| Usually painless | Yes |
| Can cause discomfort or pain | Yes |
| Can become infected | Yes |
| May require medical intervention | Yes |
| Can lead to complications | Yes |
| Can be treated with warm compresses | Yes |
| May require drainage or surgery | Yes |
| Can recur after treatment | Yes |
| Rarely affect pregnancy or delivery | Yes |
What You'll Learn
- Can bartholin cysts pose any risks to the health of a pregnant woman?
- Can a bartholin cyst during pregnancy cause any complications during childbirth?
- What is the likelihood of a bartholin cyst becoming infected while pregnant?
- Are there any potential treatment options for bartholin cysts that are safe to use during pregnancy?
- Are there any preventative measures that pregnant women can take to reduce their risk of developing a bartholin cyst?

Can bartholin cysts pose any risks to the health of a pregnant woman?
Bartholin cysts are fluid-filled sacs that can develop in the Bartholin glands, which are located on either side of the vaginal opening. These cysts can cause discomfort and pain, especially during sexual activity and walking. While bartholin cysts are generally harmless and do not pose any significant risks to the health of a pregnant woman, they can still cause inconvenience and discomfort.
During pregnancy, hormonal changes can lead to increased production of fluid in the Bartholin glands, leading to the formation of cysts. However, these cysts do not usually pose any risks to the woman or her baby. They are typically benign and resolve on their own without any medical intervention. In rare cases, the cyst may become infected, causing an abscess to develop. This can result in more severe discomfort and require medical treatment.
If a pregnant woman develops a bartholin cyst, it is important for her to monitor the cyst and inform her healthcare provider about any changes in size, pain, or discomfort. The healthcare provider can then assess the cyst and determine if any intervention, such as draining the cyst or prescribing antibiotics, is necessary. It is essential to seek medical attention if the cyst becomes painful, infected, or interferes with daily activities.
In some cases, if the cyst does not resolve on its own or becomes recurrent, surgical intervention may be required. However, this is generally avoided during pregnancy unless absolutely necessary. Most healthcare providers will opt for conservative management and wait until after delivery to address the cyst, as surgery during pregnancy carries risks.
Preventive measures can be taken to minimize the risk of developing bartholin cysts during pregnancy. These include maintaining good hygiene by cleaning the genital area regularly, avoiding harsh soaps or cleansers that can irritate the skin, and practicing safe sexual practices to reduce the risk of infection. Wearing breathable underwear and avoiding tight clothing can also help prevent the development of cysts.
In summary, bartholin cysts do not pose any significant risks to the health of a pregnant woman. However, they can cause discomfort and inconvenience. It is important for a pregnant woman to monitor any changes in the cyst and inform her healthcare provider. In most cases, the cyst will resolve on its own without the need for medical intervention. If intervention is necessary, healthcare providers will generally opt for conservative management and avoid surgery during pregnancy unless absolutely necessary. Preventive measures can also be taken to minimize the risk of developing bartholin cysts during pregnancy.
The Milestone Moment: When Does a Baby Drop During Pregnancy?
You may want to see also

Can a bartholin cyst during pregnancy cause any complications during childbirth?
During pregnancy, many women experience various changes and discomforts in their bodies. One common issue that can arise is the development of a Bartholin cyst. This cyst, which forms on one of the Bartholin's glands located on either side of the vaginal opening, can cause discomfort and concern for expectant mothers. However, in most cases, a Bartholin cyst during pregnancy does not cause any complications during childbirth.
A Bartholin cyst is a fluid-filled sac that forms when the ducts of the Bartholin glands become blocked. These glands produce a small amount of fluid that helps lubricate the vaginal opening. When the ducts become blocked, the fluid accumulates and forms a cyst. The exact cause of these blockages is not fully understood, but it is believed to be related to hormonal changes or bacterial infections.
While a Bartholin cyst can cause discomfort and pain, it typically does not pose any significant risks to a woman or her baby during childbirth. The cyst itself is not connected to the birth canal or the baby's development. It is important, however, to monitor the size and symptoms of the cyst throughout pregnancy. In rare cases, a Bartholin cyst can become infected or enlarge significantly, leading to potential complications.
If a Bartholin cyst becomes infected during pregnancy, it can cause symptoms such as increased pain, redness, and swelling. In some cases, an infected cyst may require medical intervention, such as antibiotics or drainage. It is essential for pregnant women to seek medical advice if they experience any concerning symptoms associated with their Bartholin cyst.
In terms of childbirth, a Bartholin cyst should not impede the delivery process. Obstetricians are experienced in managing various conditions that may arise during childbirth and can address any concerns related to the cyst. It is important to communicate with healthcare providers about the presence of a Bartholin cyst to ensure that they are aware and can provide appropriate care and guidance during labor and delivery.
In conclusion, while a Bartholin cyst can cause discomfort and pain during pregnancy, it typically does not cause complications during childbirth. It is important for pregnant women to monitor the size and symptoms of the cyst and seek medical advice if any concerning symptoms arise. Obstetricians are well-equipped to manage and address any issues related to Bartholin cysts during labor and delivery, ensuring a safe and successful childbirth experience.
Exploring the Possibility of Ectopic Pregnancy After Hysterectomy: What You Need to Know
You may want to see also

What is the likelihood of a bartholin cyst becoming infected while pregnant?
Bartholin cysts are a common condition in women, which can sometimes occur during pregnancy. These cysts are fluid-filled sacs that form on the Bartholin's glands, located on either side of the vaginal opening. While most Bartholin cysts are harmless and painless, there is a risk of infection, especially during pregnancy.
During pregnancy, hormonal changes can affect the Bartholin's glands, leading to an increased risk of cyst formation. The cyst itself is usually not a cause for concern, but if it becomes infected, it can cause pain, swelling, and discomfort.
The likelihood of a Bartholin cyst becoming infected during pregnancy can vary depending on several factors. These include the size of the cyst, the overall health of the pregnant woman, and any existing medical conditions she may have. Additionally, poor hygiene practices can also increase the risk of infection.
If a Bartholin cyst becomes infected during pregnancy, it is important to seek medical attention promptly. Untreated infections can lead to complications, such as abscess formation or the spread of infection to nearby tissues.
The treatment for an infected Bartholin cyst during pregnancy will depend on the severity of the infection and the gestational age of the woman. In most cases, a course of antibiotics will be prescribed to help clear the infection. Warm compresses can also be applied to the affected area to help reduce pain and swelling.
In some cases, if the infection is severe or does not respond to conservative treatment, a procedure known as marsupialization may be recommended. Marsupialization involves creating a small incision in the cyst to allow drainage and facilitate healing.
It is worth noting that preventing a Bartholin cyst from becoming infected during pregnancy is possible with proper hygiene practices. This includes keeping the genital area clean and dry, wearing breathable underwear, and avoiding irritating substances or products.
In conclusion, while Bartholin cysts can occur during pregnancy, the likelihood of them becoming infected can vary. Factors such as cyst size, overall health, and hygiene practices can all influence the risk of infection. Prompt medical attention and appropriate treatment are crucial if an infection occurs to prevent complications. Maintaining good hygiene practices can help reduce the risk of infection in the first place.
Choosing the Best Unisom for Pregnancy: A Comprehensive Guide
You may want to see also

Are there any potential treatment options for bartholin cysts that are safe to use during pregnancy?
Bartholin cysts are fluid-filled sacs that develop in the Bartholin glands, which are located near the opening of the vagina. These cysts can cause discomfort and pain, especially during pregnancy when there are already numerous changes occurring in the body. It is important for pregnant women to find safe and effective treatment options for Bartholin cysts to prevent any complications or discomfort.
During pregnancy, the hormonal changes can increase the likelihood of developing Bartholin cysts. The increased levels of estrogen can cause the Bartholin glands to become blocked, leading to the formation of cysts. It is essential for pregnant women to seek treatment options that are safe for both the mother and the developing fetus.
One of the first steps in managing Bartholin cysts during pregnancy is to practice good hygiene. Pregnant women should clean the affected area gently with mild soap and warm water. Regular cleansing can help to reduce the risk of infection and promote healing. It is important to avoid using harsh soaps or perfumed products, as they can irritate the cyst and worsen the symptoms.
Hot compresses can also be used as a safe and effective treatment for Bartholin cysts during pregnancy. Applying a warm compress to the affected area for about 10-15 minutes several times a day can help to reduce pain and promote drainage of the cyst. The warm temperature can also improve blood circulation in the area, which can aid in healing.
In some cases, a healthcare provider may recommend a sitz bath for pregnant women with Bartholin cysts. A sitz bath involves soaking the pelvic area in warm water, which can help to soothe the cyst and promote healing. It is essential to ensure that the water is not too hot, as excessive heat can pose risks to the fetus.
If the cyst becomes infected or does not respond to conservative treatment options, a healthcare provider may consider draining the cyst. This procedure, known as marsupialization, involves creating a small incision in the cyst to allow the fluid to drain. It is important for pregnant women to discuss the risks and benefits of this procedure with their healthcare provider before proceeding.
In rare cases where the Bartholin cyst becomes extremely large or causes severe pain, a healthcare provider may consider surgical removal of the cyst during pregnancy. This procedure is typically performed using local anesthesia to minimize risks to the fetus. It is important for pregnant women to discuss their options with a healthcare provider and weigh the potential risks and benefits before proceeding with surgery.
In conclusion, there are several safe and effective treatment options for Bartholin cysts during pregnancy. Good hygiene practices, such as regular cleansing with mild soap and warm water, can help to reduce the risk of infection and promote healing. Hot compresses and sitz baths can also provide relief and promote drainage of the cyst. In more severe cases, draining the cyst or surgical removal may be necessary, but these options should be carefully considered and discussed with a healthcare provider. Ultimately, the treatment approach should prioritize the safety and well-being of both the mother and the developing fetus.
Understanding the Risk of Ectopic Pregnancy for Natural Conception: What You Need to Know
You may want to see also

Are there any preventative measures that pregnant women can take to reduce their risk of developing a bartholin cyst?
Bartholin cysts are a common condition that can occur during pregnancy. These cysts develop when the Bartholin's glands, which are located on either side of the vaginal opening, become blocked and filled with fluid. While there is no surefire way to prevent the development of a Bartholin cyst, there are several steps pregnant women can take to reduce their risk.
First and foremost, maintaining good hygiene is essential in preventing Bartholin cysts. Pregnant women should clean the genital area gently with warm water and mild soap. It is important to avoid using harsh soaps or douches, as they can disrupt the natural balance of bacteria in the vagina and increase the risk of infection.
Another important preventive measure is wearing loose and breathable underwear. Tight-fitting underwear or clothing can create friction and increase the likelihood of developing a cyst. Opting for cotton underwear can help keep the genital area dry and reduce the chances of infection.
Furthermore, avoiding excessive pressure or trauma to the vaginal area can help prevent the blockage of the Bartholin's glands. Pregnant women should be cautious when engaging in activities that put pressure on the genital area, such as cycling or horseback riding. If engaging in these activities cannot be avoided, it is advisable to use protective equipment and take breaks to alleviate pressure.
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is also crucial in reducing the risk of Bartholin cysts. A well-balanced diet, regular exercise, and adequate hydration can help strengthen the immune system and promote overall vaginal health. Additionally, avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can help reduce the risk of infection and inflammation in the Bartholin's glands.
Lastly, pregnant women should practice safe sex to reduce their risk of developing sexually transmitted infections (STIs), which can increase the likelihood of developing Bartholin cysts. Using barrier methods, such as condoms, can help prevent the transmission of STIs and reduce the risk of cyst formation.
In conclusion, while it is not always possible to prevent the development of Bartholin cysts during pregnancy, there are several preventive measures pregnant women can take to reduce their risk. Maintaining good hygiene, wearing loose and breathable underwear, avoiding excessive pressure or trauma to the vaginal area, practicing a healthy lifestyle, and practicing safe sex can all contribute to a decreased risk of Bartholin cysts. It is important for pregnant women to consult with their healthcare provider for personalized advice and guidance on reducing their risk of developing this condition.
The Perfect Diet for Managing Diabetes During Pregnancy
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
No, Bartholin cysts are typically not dangerous during pregnancy. They are common and benign cysts that form near the openings of the Bartholin's glands in the vagina. Although they can be uncomfortable and cause pain, they do not pose a significant risk to the health of the mother or the baby.
In most cases, Bartholin cysts do not affect a woman's ability to give birth vaginally. However, if the cyst becomes infected or grows significantly in size, it may cause obstruction or discomfort during labor. In such cases, a healthcare provider may recommend draining or surgically removing the cyst before delivery.
While Bartholin cysts themselves are unlikely to cause complications during pregnancy, if they become infected, there is a risk of developing an abscess. An abscess is a painful, pus-filled pocket that requires medical attention. If you suspect your Bartholin cyst has become infected, it is important to seek medical advice to prevent complications.
Treatment for Bartholin cysts during pregnancy typically depends on the severity of the symptoms and whether the cyst is causing any discomfort or complications. In many cases, conservative management such as warm compresses and sitz baths can help to alleviate symptoms. However, if the cyst becomes infected or causes significant pain or obstruction, a healthcare provider may recommend incision and drainage or surgical removal of the cyst. It is important to consult with your healthcare provider for appropriate management during pregnancy.







